2D Advection-Diffusion equation
in this notebook we provide a simple example of the DeepMoD algorithm and apply it on the 2D advection-diffusion equation.
# General imports
import numpy as np
import torch
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
# DeepMoD functions
from deepymod import DeepMoD
from deepymod.model.func_approx import NN
from deepymod.model.library import Library2D
from deepymod.model.constraint import LeastSquares
from deepymod.model.sparse_estimators import Threshold,PDEFIND
from deepymod.training import train
from deepymod.training.sparsity_scheduler import TrainTestPeriodic
from scipy.io import loadmat
# Settings for reproducibility
np.random.seed(42)
torch.manual_seed(0)
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
Prepare the data
Next, we prepare the dataset.
data = loadmat('data/advection_diffusion.mat')
usol = np.real(data['Expression1'])
usol= usol.reshape((51,51,61,4))
x_v= usol[:,:,:,0]
y_v = usol[:,:,:,1]
t_v = usol[:,:,:,2]
u_v = usol[:,:,:,3]
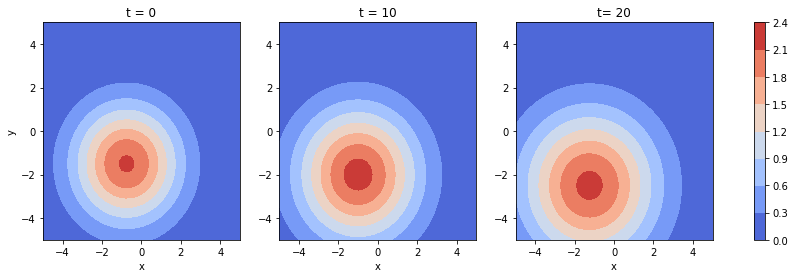
Next we plot the dataset for three different time-points
fig, axes = plt.subplots(ncols=3, figsize=(15, 4))
im0 = axes[0].contourf(x_v[:,:,0], y_v[:,:,0], u_v[:,:,0], cmap='coolwarm')
axes[0].set_xlabel('x')
axes[0].set_ylabel('y')
axes[0].set_title('t = 0')
im1 = axes[1].contourf(x_v[:,:,10], y_v[:,:,10], u_v[:,:,10], cmap='coolwarm')
axes[1].set_xlabel('x')
axes[1].set_title('t = 10')
im2 = axes[2].contourf(x_v[:,:,20], y_v[:,:,20], u_v[:,:,20], cmap='coolwarm')
axes[2].set_xlabel('x')
axes[2].set_title('t= 20')
fig.colorbar(im1, ax=axes.ravel().tolist())
plt.show()
We flatten it to give it the right dimensions for feeding it to the network:
X = np.transpose((t_v.flatten(),x_v.flatten(), y_v.flatten()))
y = np.float32(u_v.reshape((u_v.size, 1)))
We select the noise level we add to the data-set
noise_level = 0.01
y_noisy = y + noise_level * np.std(y) * np.random.randn(y.size, 1)
Select the number of samples:
number_of_samples = 1000
idx = np.random.permutation(y.shape[0])
X_train = torch.tensor(X[idx, :][:number_of_samples], dtype=torch.float32, requires_grad=True)
y_train = torch.tensor(y[idx, :][:number_of_samples], dtype=torch.float32)
Configuration of DeepMoD
Configuration of the function approximator: Here the first argument is the number of input and the last argument the number of output layers.
network = NN(3, [50, 50, 50,50], 1)
Configuration of the library function: We select athe library with a 2D spatial input. Note that that the max differential order has been pre-determined here out of convinience. So, for poly_order 1 the library contains the following 12 terms: * [1, u_x, u_y, u_{xx}, u_{yy}, u_{xy}, u, u u_x, u u_y, u u_{xx}, u u_{yy}, u u_{xy}]
library = Library2D(poly_order=1)
Configuration of the sparsity estimator and sparsity scheduler used. In this case we use the most basic threshold-based Lasso estimator and a scheduler that asseses the validation loss after a given patience. If that value is smaller than 1e-5, the algorithm is converged.
estimator = Threshold(0.1)
sparsity_scheduler = TrainTestPeriodic(periodicity=50, patience=10, delta=1e-5)
Configuration of the sparsity estimator
constraint = LeastSquares()
# Configuration of the sparsity scheduler
Now we instantiate the model and select the optimizer
model = DeepMoD(network, library, estimator, constraint)
# Defining optimizer
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), betas=(0.99, 0.99), amsgrad=True, lr=1e-3)
Run DeepMoD
We can now run DeepMoD using all the options we have set and the training data: * The directory where the tensorboard file is written (log_dir) * The ratio of train/test set used (split) * The maximum number of iterations performed (max_iterations) * The absolute change in L1 norm considered converged (delta) * The amount of epochs over which the absolute change in L1 norm is calculated (patience)
train(model, X_train, y_train, optimizer,sparsity_scheduler, log_dir='runs/2DAD/', split=0.8, max_iterations=100000, delta=1e-4, patience=8)
| Iteration | Progress | Time remaining | Loss | MSE | Reg | L1 norm |
7000 7.00% 3733s 1.07e-04 3.60e-05 7.08e-05 1.87e+00 Algorithm converged. Stopping training.
Sparsity masks provide the active and non-active terms in the PDE:
model.sparsity_masks
[tensor([False, True, True, True, True, False, False, False, False, False,
False, False])]
estimatior_coeffs gives the magnitude of the active terms:
print(model.estimator_coeffs())
[array([[0. ],
[0.3770935 ],
[0.7139108 ],
[0.389949 ],
[0.32122847],
[0. ],
[0. ],
[0. ],
[0. ],
[0. ],
[0. ],
[0. ]], dtype=float32)]